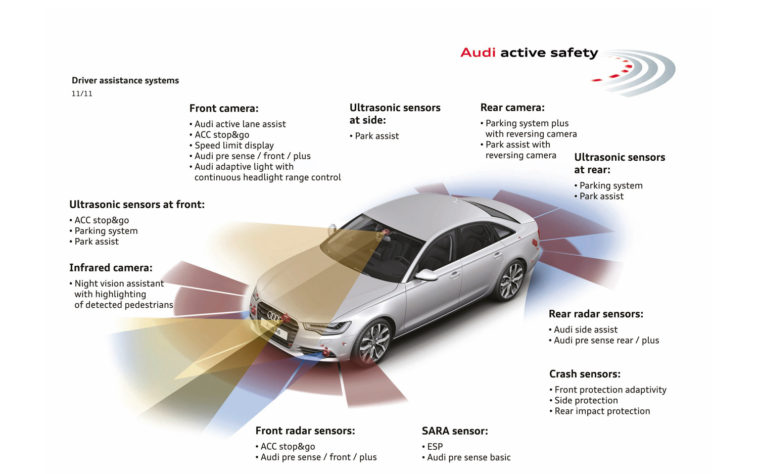
Active safety features help in avoiding or reducing the impact in an accident before it actually happens.
These features work by taking input from the car and its surrounding in real time by using various sensors. And if it detects anything unusual that can cause an accident, it assists the driver in reacting accordingly, or alerts him, or takes over the control of the vehicle according to the severity of situation.
Most of the modern come equipped with some of these features as standard as instructed by the safety regulating authorities, whereas many come in as an accessible option. These active safety features can be classified in two segments.
One segment of these active safety features helps improve the drivers control on the car in emergency situations. These can be crucial in maintaining the cars stability while maneuvering at high speeds or during braking. They mostly rely on data feed from sensors that detect the vehicle’s attributes, and sense for any emergency situation to respond accordingly. It includes Antilocking Braking System (ABS), Electronic Stability Control (ESC), Electronic Brake Distribution (EBD) and Traction Control System (TRC) etc.
- ABS ensures that the rider has complete control over the car even when it is braked harshly. When brakes are fully depressed it simply prevents the tires from locking, so the drive can manure over the obstacle.
- An ESC and EBD helps the car stay under controls while maneuvering at high speeds. It applies individual braking on corresponding tires to generate moment in order to aid the car to turn securely at high speeds.
- A TRC comes in action to avoid any tire slippage, when the rider steps down on the gas pedal, to avoid the car from going sideways and out of his control.
Other active safety features help avoid the accidents or reduce the amount of damage done by alerting the distracted driver of the situation or taking over the cars control to avoid it from happening. These Safety features take data feed from the environment through radars and cameras. And sense or predict for any inbound hazard. These type of safety features require better computers to control them, along with well-developed software to detect such road vulnerabilities. Some of the major active safety features of this type include Vehicle Lane Keeping (VLK), Autonomous Emergency Braking, Blind-Spot Detectors etc.
- Vehicle Lane Keeping senses the on-road markings and interprets the road lanes. If it detects that the car is slowly drifting off its driving lane, it alerts the driver with a beep or vibrating the steering along with reducing its speed, or it automatically brings the car back into its driving lane.
- Autonomous Emergency Braking Systems use cameras, radars or lasers to map out the vehicles, obstacles or pedestrians in the front proximity of the car. If it senses that the driver won’t be able to react in time to the obstacle Infront, it applies the emergency brakes itself automatically.
- Blind spot detectors spot obstacles in close proximity off any blind spots in the car such as Infront of its A or C pillars and alerts the driver with a beep, or vibration to avoid collisions. They also alert the driver of a side lane approaching cars by flashing a hazard light in wing mirrors, to avoid changing lane when it’s on.
The development of these active features has led to the introduction of autonomous vehicles or partially autonomous systems in vehicles for consumers such as adaptive cruise control. They can be termed as more of a comfort feature as compared to the safety features mentioned above.
Active safety features are worth adding in consumer vehicles for added safety and are ensured to come as standard from manufacturers by safety regulation authorities.